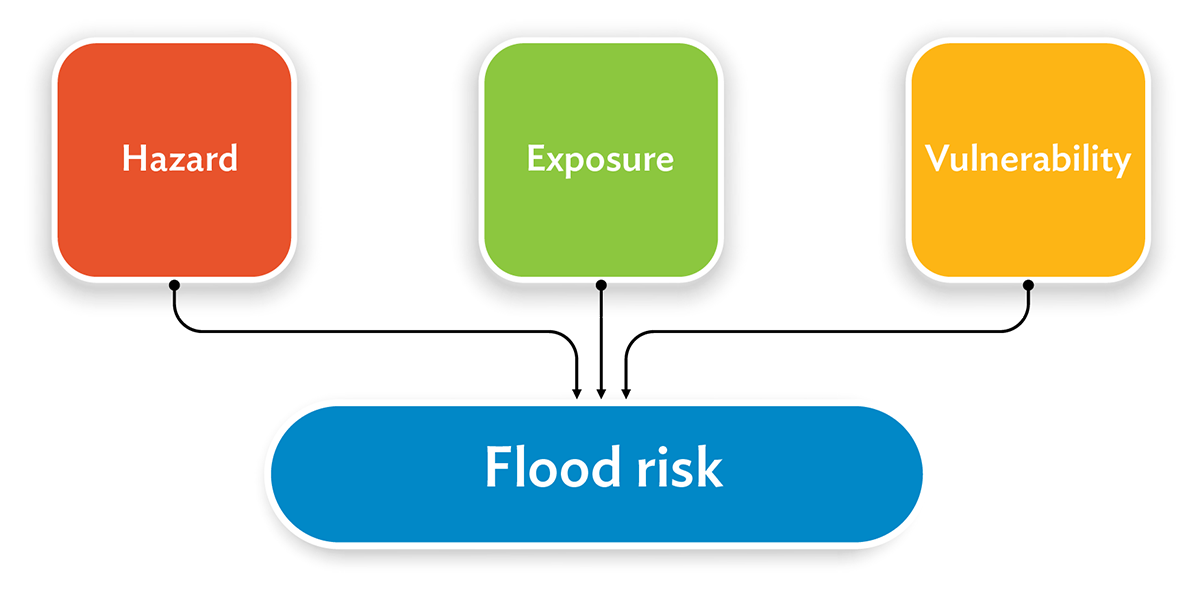
Flood risk is normally described as a function of three components: hazard, exposure, and vulnerability.
Source: Asian Development Bank. Strengthening Integrated Flood Risk Management: A Practical Guide to Integrated Flood Risk Management. Consultant’s report. Manila (TA 9634-REG).
- A flood hazard is a flood event that is potentially damaging and has three main characteristics: source, magnitude (depth, velocity, and duration that causes damage), and location or extent. The magnitude of the flood hazard is usually described using the term annual exceedance probability (AEP) or return period.
- Exposure refers to people, property, assets, systems, or other elements present in flood hazard areas that are thereby subject to potential loss and damage. Since a dominating factor is the density of population and infrastructure, exposure will increase with population growth and rural-to-urban migration. Furthermore, as the quality of life increases in developing countries, so does the relative value of assets exposed and their potential loss.
- Vulnerability refers to the characteristics and circumstances of a community, system or asset that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard. High vulnerability can create large losses from even moderate hazards. In poor and highly vulnerable areas, the frequent small- or medium-scale floods can have a significant cumulative effect.